Latin american revolutions ap world history – Latin American Revolutions: A Comprehensive Exploration for AP World History delves into the intricate tapestry of the revolutionary movements that swept across Latin America, forever altering its political, economic, and social landscape. This exploration promises a comprehensive examination of the catalysts, key figures, major events, and lasting impact of these pivotal uprisings.
As we embark on this journey through Latin American history, we will uncover the profound influence of European colonialism and Enlightenment ideals on the revolutionary fervor that ignited across the region. We will encounter charismatic leaders who dared to challenge the established order, driven by ideologies ranging from independence to social reform.
Historical Context of Latin American Revolutions
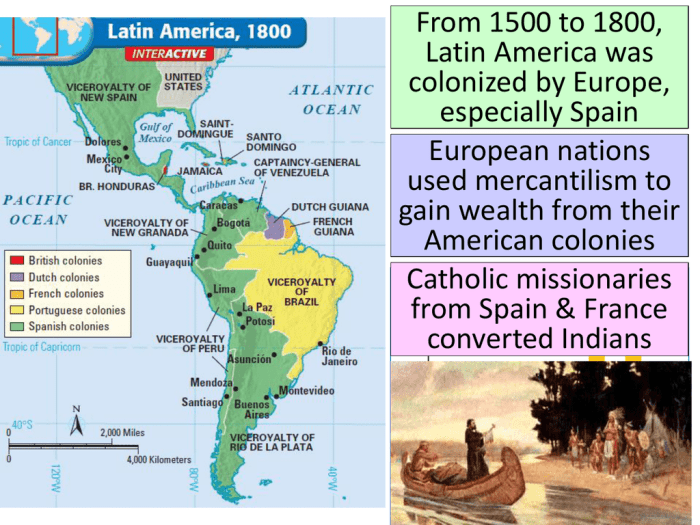
The Latin American revolutions of the early 19th century were a series of political and military conflicts that led to the independence of most of Spanish and Portuguese America from European rule. The revolutions were sparked by a complex interplay of political, economic, and social factors, including the rise of Creole nationalism, the influence of European Enlightenment ideas, and the economic and political reforms implemented by the Bourbon monarchs in Spain.
European Colonialism and Enlightenment Ideas
- European colonialism had a profound impact on the development of Latin America. The Spanish and Portuguese empires imposed their own political, economic, and social systems on the region, which led to resentment among the Creole elite.
- The Enlightenment ideas of liberty, equality, and self-determination inspired many Creole intellectuals and leaders to challenge the authority of the European powers.
Key Leaders and Ideologies: Latin American Revolutions Ap World History
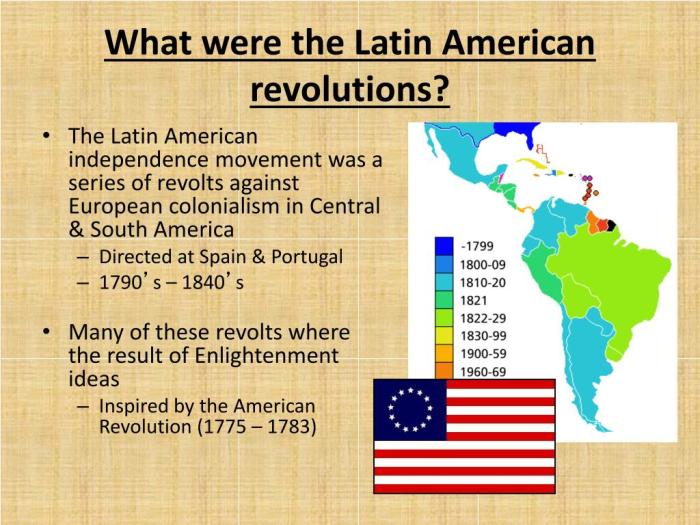
Prominent Leaders
- Simón Bolívar: Known as the “Liberator,” Bolívar led the independence movements in Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia.
- José de San Martín: A military leader from Argentina, San Martín led the liberation of Chile and Peru.
- Miguel Hidalgo: A Mexican priest who led the first major uprising against Spanish rule in Mexico.
Ideologies and Goals
- Independence: The primary goal of the revolutions was to gain independence from European rule and establish self-governing nations.
- Republicanism: Many revolutionaries were inspired by the ideals of the American and French Revolutions and sought to establish republican governments based on popular sovereignty.
- Social Reform: Some revolutionaries, particularly in Mexico and Bolivia, advocated for social reforms such as land redistribution and the abolition of slavery.
Major Events and Battles
The Latin American revolutions involved a series of major events and battles that shaped the course of the conflicts.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1810: Miguel Hidalgo’s uprising in Mexico
- 1811: Simón Bolívar’s declaration of Venezuelan independence
- 1817: José de San Martín’s crossing of the Andes into Chile
- 1821: Mexico’s independence from Spain
- 1824: Battle of Ayacucho, which sealed the independence of Peru and Bolivia
Strategies and Tactics
- Guerrilla warfare: Revolutionary forces often used guerrilla tactics, such as hit-and-run attacks, to combat the larger and better-equipped European armies.
- Political alliances: The revolutionaries formed alliances with indigenous groups and other marginalized communities to broaden their support base.
Impact of the Revolutions
Short-Term Impact
- Political: The revolutions led to the establishment of independent nations throughout Latin America.
- Economic: The revolutions disrupted trade and commerce, leading to economic instability and a decline in living standards.
- Social: The revolutions resulted in social upheaval and the rise of new political and social elites.
Long-Term Impact, Latin american revolutions ap world history
- Political: The revolutions shaped the political landscape of Latin America for centuries, leading to the development of new political systems and ideologies.
- Economic: The revolutions had a lasting impact on the economic development of Latin America, creating new opportunities for economic growth but also perpetuating economic inequalities.
- Social: The revolutions led to the emergence of new social classes and identities, as well as the development of new cultural and intellectual movements.
Comparison to Other Revolutions

Similarities
- Causes: The Latin American revolutions shared many of the same causes as other major revolutions, such as the American and French Revolutions, including the desire for independence, self-determination, and social reform.
- Ideologies: The revolutionaries in Latin America were inspired by the Enlightenment ideas of liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty.
Differences
- Complexity: The Latin American revolutions were more complex than many other revolutions due to the diversity of the region, the involvement of multiple European powers, and the presence of indigenous and African populations.
- Duration: The Latin American revolutions lasted for over a decade, much longer than other major revolutions.
Common Queries
What were the primary causes of the Latin American revolutions?
The revolutions were fueled by a complex interplay of factors, including political oppression, economic inequality, and the influence of Enlightenment ideas.
Who were some of the most influential leaders of the Latin American revolutions?
Prominent leaders included Simón Bolívar, José de San Martín, and Miguel Hidalgo, who played pivotal roles in the struggle for independence.
What were the major events and battles of the Latin American revolutions?
Key events included the Grito de Dolores, the Battle of Ayacucho, and the Mexican War of Independence.