The prisoners’ dilemma provides insights into the – The Prisoner’s Dilemma provides profound insights into the intricate interplay between cooperation and competition in human interactions. This classic game theory model unveils the complexities of decision-making when individuals face the dilemma of choosing between self-interest and collective well-being.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma has wide-ranging applications in various fields, from economics and business to social psychology and international relations. By examining its implications, we gain valuable knowledge about the factors that shape cooperation and conflict in human societies.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma and Game Theory

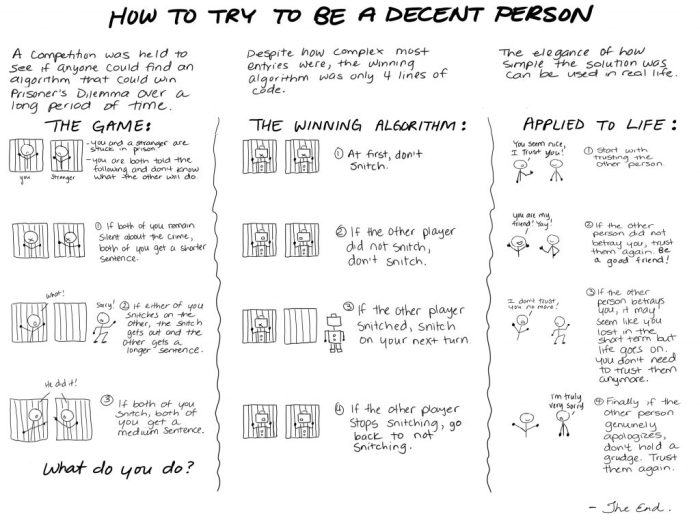
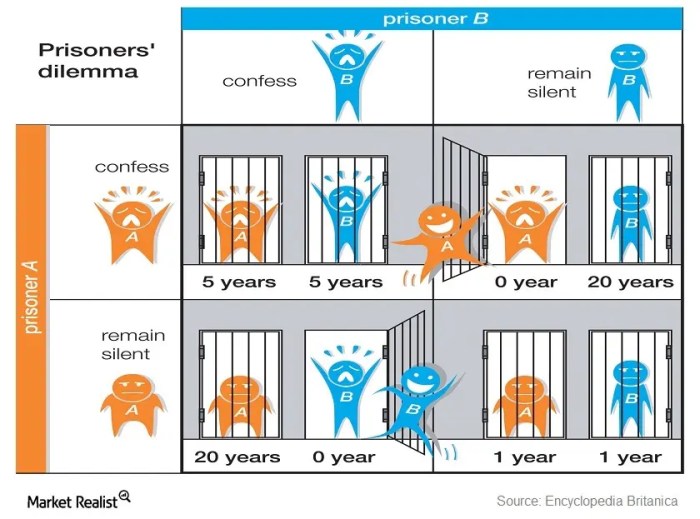
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is a classic game theory model that illustrates the tension between individual self-interest and collective well-being. It is a non-zero-sum game where the optimal outcome for an individual player is not necessarily the optimal outcome for the group as a whole.
The basic structure of the Prisoner’s Dilemma involves two players who are arrested for a crime and placed in separate interrogation rooms. Each player has the option to either cooperate with the other player by remaining silent or defect by confessing.
The possible outcomes of the game are as follows:
- If both players cooperate, they both receive a light sentence.
- If one player cooperates while the other defects, the defector receives a reduced sentence while the cooperator receives a harsh sentence.
- If both players defect, they both receive a medium sentence.
The Nash equilibrium in the Prisoner’s Dilemma is for both players to defect, even though this outcome is not optimal for the group as a whole. This is because each player has an incentive to defect regardless of what the other player does.
If one player cooperates while the other defects, the defector will receive a reduced sentence while the cooperator receives a harsh sentence. Therefore, each player is better off defecting, even though this leads to a worse outcome for both players than if they had both cooperated.
Cooperation and Competition in the Prisoner’s Dilemma, The prisoners’ dilemma provides insights into the
The Prisoner’s Dilemma highlights the challenges of cooperation in situations where individual self-interest conflicts with collective well-being. However, there are a number of factors that can influence cooperation in the Prisoner’s Dilemma, including:
- Trust and communication:When players trust each other and can communicate effectively, they are more likely to cooperate.
- Repeated interactions:If players know that they will interact with each other again in the future, they are more likely to cooperate in the present.
- Reputation:Players who have a reputation for being cooperative are more likely to be trusted and cooperated with.
There are also a number of strategies that can be used to foster cooperation in the Prisoner’s Dilemma, including:
- Tit-for-tat:This strategy involves cooperating on the first move and then matching the other player’s previous move. This strategy is effective in promoting cooperation because it punishes defectors and rewards cooperators.
- Grim trigger:This strategy involves cooperating on the first move and then defecting if the other player ever defects. This strategy is effective in deterring defection because it shows that defection will be met with retaliation.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma in Social Interactions
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is not just a theoretical game; it is also a relevant model for understanding cooperation and conflict in human relationships. For example, the Prisoner’s Dilemma can be used to explain why people sometimes cooperate even when it is not in their individual self-interest to do so.
This can be seen in situations such as when people donate to charity, volunteer their time, or help a stranger in need.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma can also be used to explain why conflict sometimes arises even when it is not in the best interests of either party. This can be seen in situations such as when people argue over resources, compete for status, or engage in destructive behavior.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma in Economics and Business
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is also a useful model for understanding competition and cooperation in economic and business contexts. For example, the Prisoner’s Dilemma can be used to analyze:
- Competition between firms in a market
- Collusion between firms
- Cooperation between firms in a supply chain
By understanding the Prisoner’s Dilemma, businesses can make better decisions about how to compete and cooperate with other firms.
Ethical Implications of the Prisoner’s Dilemma
The Prisoner’s Dilemma has a number of ethical implications. For example, the Prisoner’s Dilemma raises questions about the tension between individual self-interest and collective well-being. It also raises questions about the role of trust and communication in promoting cooperation.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is a complex and challenging game, but it can also be a valuable tool for understanding cooperation and conflict in human relationships. By understanding the Prisoner’s Dilemma, we can make better decisions about how to interact with others and how to promote cooperation.
FAQ Compilation: The Prisoners’ Dilemma Provides Insights Into The
What is the Prisoner’s Dilemma?
The Prisoner’s Dilemma is a game theory model that demonstrates the tension between individual self-interest and collective well-being. It involves two individuals who must decide whether to cooperate or defect, with the outcome depending on the choices made by both parties.
What is Nash equilibrium in the Prisoner’s Dilemma?
Nash equilibrium is a concept in game theory that describes the situation where neither player can improve their outcome by unilaterally changing their strategy. In the Prisoner’s Dilemma, the Nash equilibrium is for both players to defect, even though cooperation would lead to a better outcome for both.
How does the Prisoner’s Dilemma apply to real-world situations?
The Prisoner’s Dilemma has applications in various real-world scenarios, including international relations, business negotiations, and social interactions. It helps us understand the challenges of cooperation in situations where individuals have conflicting interests.